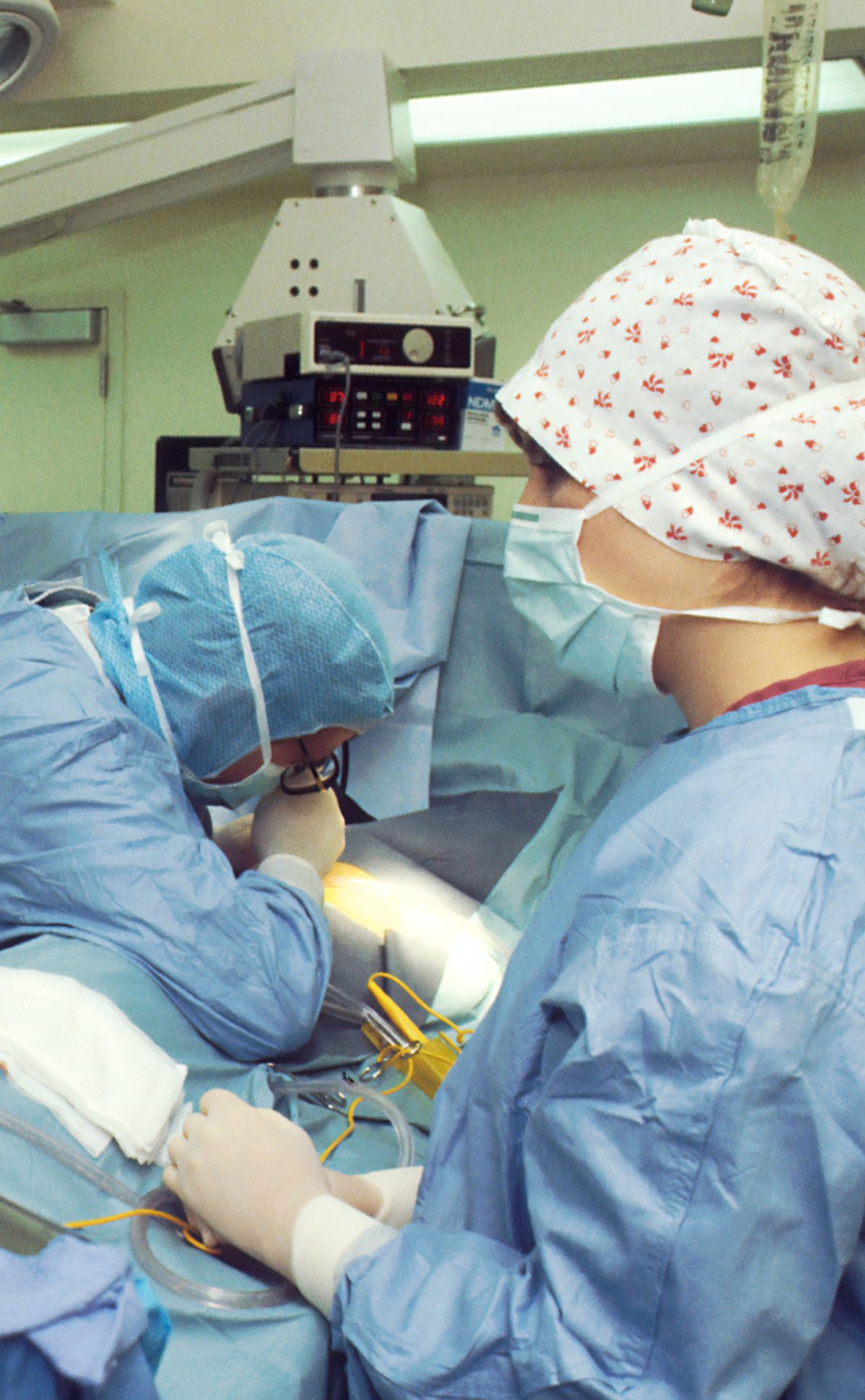
Cancer Surgery Treatments
One of the most common ways of locally treating cancer, in particular solid tumors, is through surgery. Surgeons, medical doctors, are trained to remove cancer from you body during operations.
Below, find answers to popular surgery questions and experiences of surgery shared by The Patient Story community.
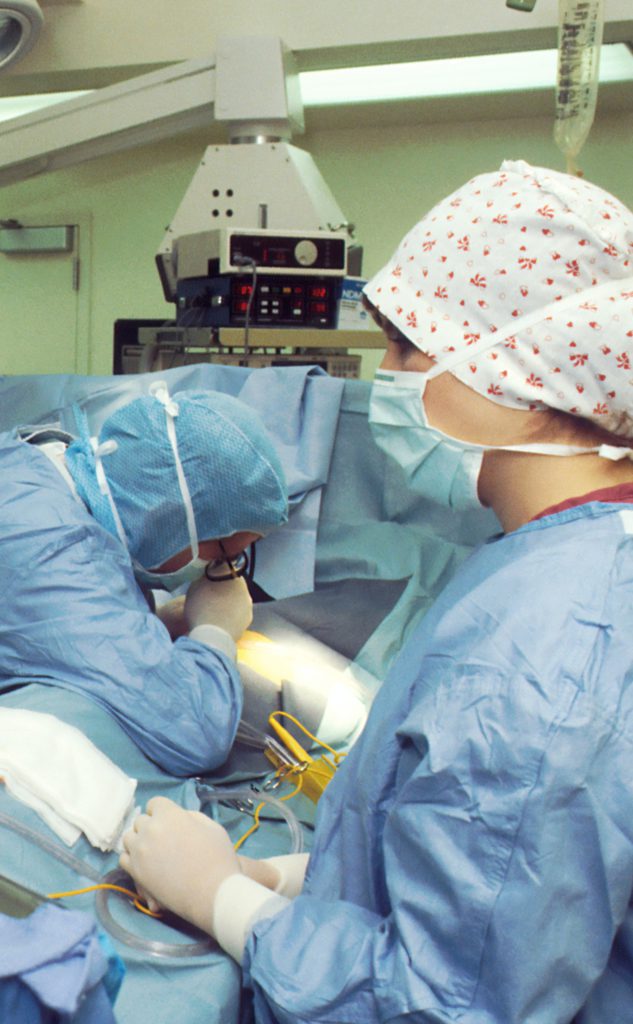
How is surgery performed?
Surgery usually requires cuts that go through skin, muscles, and sometimes bone.
Waking up from the procedure can be painful and the time for physical recovery depends on the extensiveness and size of the surgery.
Almost always, you will undergo anesthesia, drugs and other substances that make you lose feeling and/or awareness. This is meant to help prevent you from feeling pain during the operation.
Types of surgery
The many kinds of surgery are assigned based on several factors, including:
- Purpose of the surgery
- Part of body that requires surgery
- Amount of tissue
- (Sometimes) Patient preference
Surgery may be (1) open or (2) minimally invasive.
- Open surgery: Surgeon makes one large cut in order to remove the tumor, some healthy tissue, possibly close lymph nodes
- Minimally invasive surgery (laparascopic): Surgeon makes a couple to a few small cuts. In one of those small cuts, the surgeon inserts a long, thin tube with a tiny camera (laparoscope).
The surgical team sees images of inside the body from the camera, which projects onto a monitor. The surgeon uses that view to remove the tumor, some healthy tissue (margins).
Less time to recover compared to open surgery.
Types of anesthesia
- Local anesthesia: Leads to loss of feeling in one targeted area of the body
- Regional anesthesia: Leads to loss of feeling in one part of the body (e.g. arm or leg)
- General anesthesia: Leads to what feels like a very deep sleep from a total loss of feeling and a loss of awareness
Non-cutting surgeries
- Cryosurgery (or cryotherapy): Use of the extreme cold created by liquid nitrogen or argon gas to get rid of abnormal tissue.
- Cancers commonly treated: Early-stage skin cancer, retinoblastoma, precancerous growths on cervix and skin
- Cancers commonly treated: Early-stage skin cancer, retinoblastoma, precancerous growths on cervix and skin
- Lasers: Powerful beams of light cut through tissue in precise
surgeries. The lasers can also shrink and destroy cancerous growths or tumors that may become cancer. Used most commonly on body surface or internal organs’ inside lining.- Cancers commonly treated: Cervical, vaginal, esophageal, non-small cell lung cancer, basal cell carcinoma, and cervical changes that might turn into cancer.
- Cancers commonly treated: Cervical, vaginal, esophageal, non-small cell lung cancer, basal cell carcinoma, and cervical changes that might turn into cancer.
- Hyperthermia: Exposing small areas of body tissue to very high temperatures in effort to damage and destroy cancer cells. Also meant to make the cancer cells more vulnerable to radiation and chemo drugs. Still heavily researched.
- Photodynamic Therapy: Using drugs reactive to certain kinds of light. The light activates these drugs to destroy and kill nearby cancer cells. Most used to treat or alleviate symptoms of cancer, including:
How surgery destroys cancer
The purpose of surgery depends on cancer type and stage (how advanced it is).
- Completely remove the cancer: Surgery can be used to remove cancerous growths and tumors in one area.
- Debulk a tumor: This is used to remove part of a tumor to help other cancer treatments, especially when trying to remove the entire tumor may cause damage to an organ or to the body.
- Alleviate cancer symptoms: Surgery used to help lessen pain or pressure caused by tumors.
Surgery stories and experiences
Hear about different surgeries and experiences from our community of patients and survivors.
Colectomy
Sydney S., Colon Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Constant stomachaches that only went away after bowel movements, pain after eating, changes in bowel size and shape
Treatments: Surgeries (colectomy, temporary ileostomy, ileostomy reversal), chemotherapy (FOLFOX, FOLFIRI, trifluridine and tipiracil), monoclonal antibody (bevacizumab), radiation therapy, hormone therapy
...
Kailee O., Colorectal Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Sensitive stomach sometimes leading to vomiting after eating, bleeding during bowel movements, persistent fatigue, back pain, abdominal pain, anemia, significant symptom flare-up during second pregnancy
Treatments: Surgery (colectomy), chemotherapy, targeted therapy
...
Starr S., Colon Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptom: Abdominal pain
Treatments: Chemotherapy, surgeries (colectomy, hepatectomy, lymphadenectomy), targeted therapy
...
Nicole S., Colon Cancer, Stage 3
Symptoms: Dull lower abdominal pain that sharpened and was focused on the lower left side, appearance of dark blood in stool, difficulty retaining food due to near-complete blockage of sigmoid colon
Treatments: Surgery (colectomy), chemotherapy
...
Lauren G., Colon Cancer, Stage 4
Symptoms: Frequent urges to have bowel movements (up to 27x/day), incomplete evacuation, abdominal bloating
Treatments: Surgeries (colectomy, colostomy bag placement), chemotherapy
...
DIEP Flap
Krista B., IDC, Stage 1A, HR+, HER2-, ATM Mutation
Symptom: None; abnormality detected in breast MRI
Treatments: Surgery (double mastectomy with DIEP flap reconstruction), selective estrogen receptor modulator (tamoxifen)
...
Melissa H., Triple-Negative Breast Cancer, Stage 2B, IDC
Symptom: Lump in left breast
Treatments: Surgery (mastectomy), chemotherapy
...
Gasterectomy
Amy M., Stomach Cancer (Gastric Adenocarcinoma), Stage 3B
Symptoms: Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blood in stool, stomachache, trouble swallowing
Treatments: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgeries (gastrectomy, partial pancreatectomy), immunotherapy
...
Alyssa B., Stomach Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic) (Hospice Update)
Symptoms: Fatigue, elevated resting heart rate, heartburn, difficulty swallowing, weight loss
Treatments: Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, surgeries (total gastrectomy; partial esophagus removal; bilateral oophorectomy and fallopian tube removal), clinical trial
...
Niccole B., Stomach Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Stomach pain after having alcoholic drinks, eating less, slight weight loss, acid reflux, vomiting, getting full fast
Treatments: Chemotherapy (hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy or HIPEC, open HIPEC with cytoreductive surgery), surgeries (partial gastrectomy, cholecystectomy, splenectomy, partial colectomy, partial hepatectomy), radiation therapy (targeted radiation therapy), immunotherapy, targeted therapy (PARP inhibitor)
...
Arelly R., Stomach Cancer (Gastric Adenocarcinoma), Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Nausea, blood in stool, side pain, extreme fatigue, excessive burping
Treatments: Surgeries (gastrectomy, port placement), chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy (antibody-drug conjugate)
...
Dawn C., Stomach Cancer (Gastric Adenocarcinoma, Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer), CDH1+, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Persistent bloating, feeling of discomfort in the stomach area, weight loss, dehydration, feeling very full leading to vomiting, high blood pressure
Treatments: Chemotherapy (HIPEC, including through a clinical trial), surgeries (gastrectomy, splenectomy, cholecystectomy, oophorectomy, appendectomy, omentectomy, peritonectomy, lymphadenectomy), immunotherapy
...
Lumpectomy
Nicole F., DCIS, Stage 1
Symptom: Appearance of a lump in the right breast
Treatments: Surgery (lumpectomy), chemotherapy, cold caps, radiation therapy, hormone therapy (tamoxifen)
...
John C., Salivary Gland Cancer
Symptoms: Rapid weight loss, small lump under ear that became more pronounced and grew larger
Treatments: Surgeries (lumpectomy, neck dissection), radiation therapy
...
Janice C., Triple-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer, Stage 4
Symptoms: Appearance of lump in left breast near sternum, fatigue, bone and joint pain
Treatments: Surgery (lumpectomy), radiation therapy (brachytherapy), chemotherapy
...
Teresa B., Recurrent Breast Cancer (Hormone-Positive), Oral Cancer (Lip Cancer), and Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
Symptoms: Lip cancer: chapped lips & a pimple-like growth on lip, breast cancer: enlarged left breast with lump, melanoma: none
Treatments: Surgeries (bilateral mastectomy with reconstruction, lumpectomy, craniotomy, Mohs, surgery, wide local excision), hormone therapy, radiation therapy
...
Elissa K., Metastatic Breast Cancer, HER2+
Symptoms: Swollen and numb feet, discomfort while wearing shoes, severe fatigue
Treatments: Surgeries (lumpectomy, hysterectomy), chemotherapy, antibody-drug conjugates, targeted therapy (monoclonal antibody), radiation therapy
...
Mastectomy
Deb O., Breast Cancer (De Novo Triple Positive and ER+ HER-)
Symptoms: First instance: appearance of lump that later on increased in size, orange peel-like skin around inverted nipple, persistent ache under right arm; second instance: appearance of lump
Treatments: First instance: chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy; second instance: surgery (mastectomy), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, CDK 4/6 inhibitor
...
Tammy U., Metastatic Breast Cancer, Stage 4
Symptoms: Severe back pain, right hip pain, left leg pain
Treatments: Surgeries (mastectomy, hip arthroplasty), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapies (CDK4/6 inhibitor, antibody-drug conjugate)
...
Nicole B., Triple-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Appearance of lumps in breast and liver, electric shock-like sensations in breast, fatigue
Treatments: Chemotherapy, surgeries (installation of chemotherapy port, mastectomy with flat aesthetic closure), targeted therapy (antibody-drug conjugate), hyperbaric oxygen therapy, lymphatic drainage
...
Teresa B., Recurrent Breast Cancer (Hormone-Positive), Oral Cancer (Lip Cancer), and Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
Symptoms: Lip cancer: chapped lips & a pimple-like growth on lip, breast cancer: enlarged left breast with lump, melanoma: none
Treatments: Surgeries (bilateral mastectomy with reconstruction, lumpectomy, craniotomy, Mohs, surgery, wide local excision), hormone therapy, radiation therapy
...
Maria S., Breast Cancer, Stage 4
Symptoms: Intermittent but severe pain including a burning sensation on the side of the breast, appearance of a cyst and a lump, abnormally warm and pink-colored breast, nipple inversion, strangely liquid menstrual periods, unusual underarm odor, darkening and dimpling of the nipple, severe fatigue, night sweats
Treatments: Chemotherapy, surgeries (mastectomy, lymphadenectomy), radiation therapy, targeted therapy
...
Orchiectomy
Ryan L., Testicular Cancer (Metastatic)
Symptoms: Strange feeling in lower back one night, left testicle swollen to twice normal size
Treatments: Surgery (orchiectomy), chemotherapy
...
Andrew Ryan P., Testicular Cancer, Stage 4 (Metastatic)
Symptom: Severe leg pain
Treatments: Surgeries (retroperineal lymph node dissection or RPLND, orchiectomy, lung resection), chemotherapy, stem cell transplant
...
Matt B., Testicular Cancer (Embryonal Carcinoma, Metastatic)
Symptoms: Severe lower back pain, loss of sensation in left leg, dizziness, fatigue, night sweats, heart complications
Treatments: Surgeries (retroperitoneal lymph node dissection or RPLND, orchiectomy, liver resection, hernia repair surgery), chemotherapy
...
Rob K., Testicular Cancer, Stage 3C
Symptoms: Persistent back pain, loss of appetite, vomiting blood, fatigue, firmness in one testicle
Treatments: Chemotherapy, surgeries (orchiectomy & retroperitoneal lymph node dissection)
...
Shawn H., Testicular Cancer (Seminoma and Non-Seminoma), Stage 3C
Symptom: Discomfort in testicular area
Treatment: Surgery (orchiectomy), chemotherapy
...
References: